Adderall is a widely prescribed medication, primarily used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Narcolepsy. With its stimulant properties, it enhances focus, improves attention span, and can help with daytime sleepiness.
But as with all medications, people often find themselves asking how long it stays in the system. This question is crucial, whether you’re considering the medication’s effectiveness, concerned about drug testing, or simply curious about its duration in your body.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore various factors influencing how long it remains in your system. We’ll dive into the science behind its metabolism, its half-life, and the variables that can affect its elimination.
Additionally, we’ll address common questions related to drug testing and potential side effects. Whether you’re a patient, a concerned friend or family member, or simply inquisitive, this guide will answer your questions and provide valuable insight into how it interacts with the body.
This blog will equip you with the knowledge to better manage the use of this medication and ensure your health and safety. Let’s break down the key points of how long it stays in your system and what factors impact its presence in your body.
The Basics: What Is Adderall?
It is a combination of two stimulant medications: amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. These chemicals work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, including dopamine and norepinephrine. As a result, it improves focus, increases alertness, and reduces impulsivity. It is commonly prescribed for ADHD and narcolepsy, conditions where individuals experience challenges with focus, attention, and daytime drowsiness.
When taken, it is metabolized by the liver and eventually excreted by the kidneys. The exact amount of time it stays in the body can vary based on numerous factors. Understanding these factors can help answer the question, “How long does it stay in your system?”
The Half-Life of Adderall
The term “half-life” refers to the amount of time it takes for half of the drug to leave the body. For Adderall, the half-life varies depending on whether you’re taking the immediate-release or extended-release version.
- Immediate-Release: The half-life of immediate-release it is typically between 9 and 14 hours. This means that, on average, it will take around 9 to 14 hours for half of the drug to be eliminated from your system.
- Extended-Release (Adderall XR): The half-life of Adderall XR is slightly longer, ranging from 10 to 13 hours.
It’s important to note that these are averages, and individual variations can occur depending on various factors, such as metabolism and overall health.
Adderall Results from the Pill Identifier
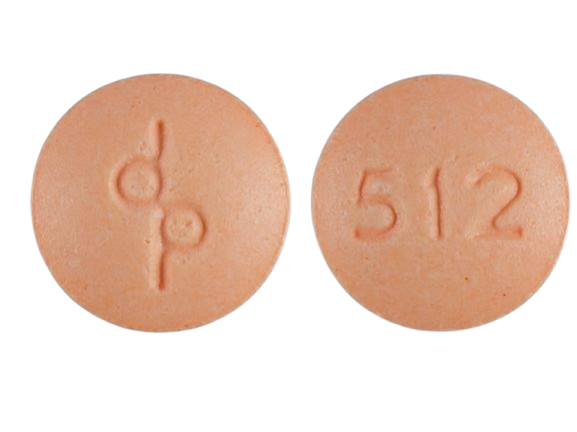
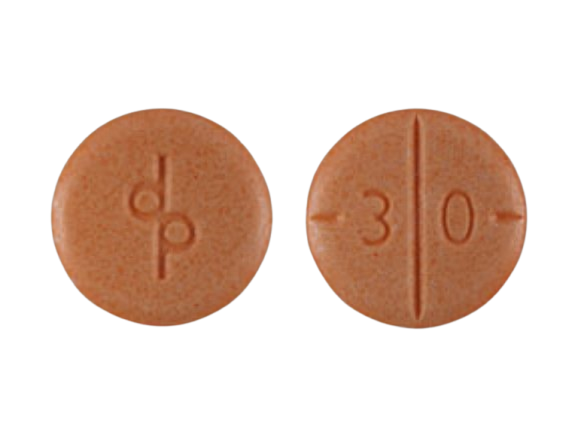

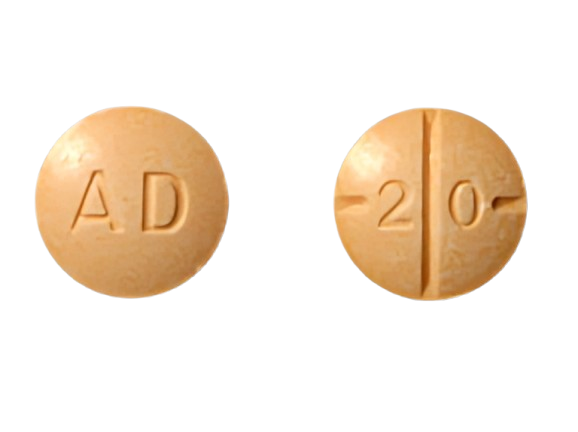

If you’ve ever come across a pill and wondered whether it’s Adderall, the Pill Identifier tool is your go-to resource. Input the pill’s shape, color, and any imprint codes to determine if it’s indeed it. Common Adderall pills include:
- Adderall (amphetamine/dextroamphetamine): 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg are the most commonly prescribed doses.
- Adderall XR (extended-release): Available in 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, and 30 mg.
The Pill Identifier is often used by pharmacists, doctors, and patients to verify medications, ensuring proper identification and dosage.
Adderall Dosage for ADHD (Immediate-Release):
For those using Adderall IR to treat ADHD, the starting dose for adults is usually 5 mg once or twice daily, with adjustments based on effectiveness and side effects. Typically, the maximum dose for adults is 40 mg per day. For children aged 6 and older, the starting dose is usually 5 mg per day.
Adderall Dosage for Narcolepsy (Immediate-Release):
The starting dose for adults with narcolepsy is typically 10 mg once or twice daily, increasing based on individual response and tolerance. The maximum dose is generally 60 mg per day.
Adderall Dosage for Children (IR):
For children, the dose is carefully adjusted. The usual range is between 5 to 30 mg per day, with the total dose split into one or two administrations per day.
Adderall XR Dosage Guide
Adderall XR (Extended-Release) Dosage for ADHD:
Adderall XR provides a more gradual release of the medication, offering extended effects throughout the day. The starting dose for adults is usually 20 mg once daily in the morning, and for children over 6 years old, it’s typically 5 mg to 10 mg once daily. The dose can be gradually increased by 5 mg to 10 mg per week, with the maximum dose generally being 40 mg per day for both adults and children.
For Narcolepsy:
The starting dose for Adderall XR in narcolepsy is 20 mg once daily in the morning, with dosage adjustments based on clinical response.
Adderall vs. Adderall XR: What’s the Difference?
It comes in Immediate-Release (IR) and Extended-Release (XR). Here’s how they compare:
| Feature | Adderall (IR) | Adderall XR |
| Duration of Action | 4–6 hours | 10–12 hours |
| Dosing Frequency | 2–3 times per day | Once daily (morning) |
| Onset of Action | 30–60 minutes | 30–60 minutes |
| Ideal Use | Shorter duration of effect, more flexibility in dose timing | Once-daily use for extended effect |
Which Should You Choose?
The choice between Adderall and Adderall XR largely depends on lifestyle and needs. Those who need consistent medication throughout the day might prefer the XR form, which only requires a single dose in the morning. On the other hand, individuals who don’t mind taking the medication multiple times a day or who need more flexibility may opt for the IR version.
Adderall Side Effects:
Like any medication, it comes with potential side effects. Here’s a breakdown:
Common Side Effects:
- Dry mouth
- Loss of appetite
- Insomnia
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Headaches
- Dizziness
These side effects are often temporary and subside as your body adjusts to the medication.
Severe Side Effects:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Irregular heartbeat
- Psychosis, paranoia, or aggression
- Severe allergic reactions (e.g., swelling, rash, trouble breathing)
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these severe reactions.
Long-Term Side Effects:
- Growth suppression in children (monitored with regular check-ups)
- Mental health issues, including the worsening of anxiety, depression, or aggression.
- Tolerance and dependence: Over time, some people may develop a tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect. This increases the risk of misuse.
Adderall Interactions Checker
It may interact with various medications, which can either increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of the drug. Always use the it before starting any new medication. Some key interactions include:
- MAO inhibitors (e.g., isocarboxazid, phenelzine): Combining these with it can cause severe hypertension or even a life-threatening condition.
- Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs): May increase serotonin levels, leading to serotonin syndrome.
- Blood pressure medications: Since it can increase blood pressure, it may interfere with blood pressure-lowering medications.
Make sure to consult your doctor or pharmacist before combining it with any other medication.
Adderall Support Group
Support groups can be an invaluable resource for individuals using it to manage ADHD or narcolepsy. These groups provide a space for patients to share experiences, ask questions, and offer support to one another. Whether in person or online, joining an Adderall support group can help you better understand the medication, manage side effects, and stay informed about new treatment options.
You can find support groups through mental health organizations or online communities like Reddit or Facebook.
Adderall Shortage Information
In recent years, Adderall shortages have become a common issue in the United States, leading to difficulty accessing the medication for those who rely on it. These shortages have been caused by a combination of increased demand, supply chain issues, and regulatory limitations on manufacturing.
The FDA and drug manufacturers are working to address the shortage, but it’s important to stay in contact with your healthcare provider to explore alternative treatments or adjust your medication as needed during times of shortage. If you are unable to find it, your doctor may recommend an alternative stimulant or non-stimulant medication for managing ADHD or narcolepsy.
People Also Search About
- What is Tapentadol? A Complete Guide to Its Uses, Benefits, and Risks
- How Long Does Tramadol Stay in Your System?
- Tramadol vs Oxycodone: Which Painkiller is More Effective?
Final Words
It is a highly effective medication for treating ADHD and narcolepsy, but like all medications, it requires careful management.
Whether you’re considering Adderall for the first time or have been using it for years, understanding the dosages, side effects, potential drug interactions, and available support systems can help you make the most informed decisions about your treatment.
Always work closely with your healthcare provider to ensure that Adderall is the right medication for your needs, and stay informed about any changes or shortages that might affect your treatment.

2 thoughts on “How Long Does Adderall Stay in Your System? A Complete Guide”